Skin conditions and rashes often induce discomfort and concern, triggering a quest for answers and relief. Among the myriad skin ailments, distinguishing between bed bug bites and shingles is paramount.
Bed bug bites and shingles rashes share similar characteristics, such as redness, itching, and blistering, but their underlying causes and treatments differ significantly. Misidentification can lead to misguided remedies and prolonged suffering.
This article serves the crucial purpose of equipping readers with the knowledge to recognize the subtle yet critical distinctions between these conditions. By understanding the nuances, individuals can seek appropriate care promptly, alleviating discomfort and enhancing their overall well-being.
So, let’s begin.
Bed Bug Bites
Description of appearance and common locations:
Bed bug bites typically appear as small, red, and raised welts on the skin. They often occur in clusters or lines resembling a zigzag pattern.
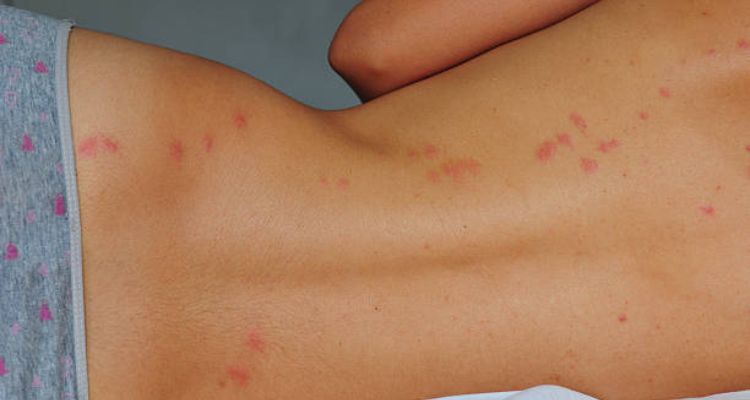
Bed bug bites are commonly found on exposed skin areas such as the arms, shoulders, neck, back and legs. These tiny, blood-feeding insects are nocturnal, and their bites can go unnoticed until the itchy symptoms emerge.
Characteristics of the itching and discomfort associated with bed bug bites:
Bed bug bites are notorious for causing intense itching. This itching sensation often begins a few days after the initial bite and can persist for several days or weeks. Scratching can lead to secondary infections, making prompt identification and management crucial.
Factors that may indicate a bed bug infestation in addition to bites:
Aside from bites, signs of a bed bug infestation may include the presence of small reddish-brown bugs in crevices and seams of mattresses or furniture, tiny white eggs, and small dark fecal spots on bedding or upholstery.
Plus, some individuals may notice a sweet, musty odor in infested areas, indicating bed bugs. Early detection is key to preventing a widespread infestation.
Shingles
Introduction to shingles as a viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus:
Shingles, caused by the varicella-zoster virus (the same virus responsible for chickenpox), is a painful viral infection. After an initial chickenpox infection, the virus remains dormant in nerve cells and can later reactivate as shingles, usually in adulthood.
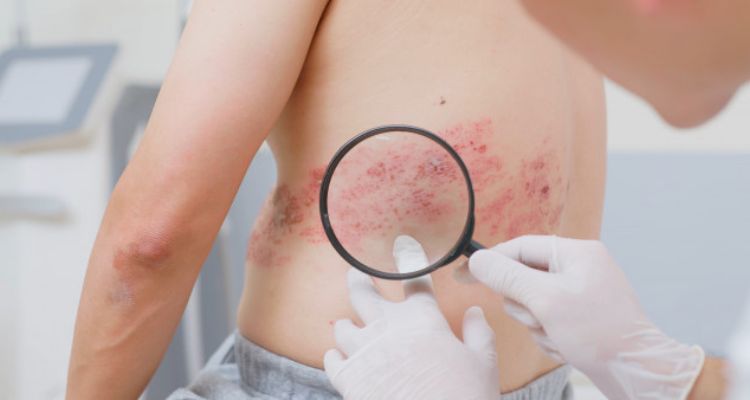
Explanation of the rash associated with shingles, including its appearance and location:
The hallmark of shingles is a blistering rash that typically appears unilaterally, wrapping around one side of the torso in a band-like pattern. The rash consists of small, fluid-filled blisters on a red base, often accompanied by burning or shooting pain.
The timeline of shingles symptoms, from tingling to blistering:
Shingles symptoms typically progress in stages. It often begins with tingling, itching, or burning sensations in a specific area of the skin. Within a few days, a red rash emerges, followed by the formation of fluid-filled blisters.
The blisters can break open, crust over, and eventually heal, with the entire process lasting several weeks. Early antiviral treatment can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
Key Differences in Appearance
Visual comparison of bed bug bites and shingles rash:
Bed bug bites typically manifest as clusters of small, red welts in zigzag patterns on exposed skin. In contrast, a shingles rash appears as a unilateral, band-like arrangement of fluid-filled blisters on a reddened base.
Highlighting distinctive features such as pattern, size, and texture:
Bed bug bites are small, often uniform in size, and tend to be flat or slightly raised. Shingles blisters are larger, irregularly shaped, and have a distinct 3D appearance, resembling a cluster of bubbles.
Location of Bites/Rash
Discussion of the typical locations on the body where bed bug bites occur:
Bed bug bites tend to cluster on exposed skin areas, often affecting the arms, shoulders, neck, and legs. They prefer to feed in areas where the skin is closest to their hiding places, such as bedding or upholstery.
Explanation of the dermatomes associated with shingles and the areas they affect:
Shingles follow specific nerve pathways called dermatomes. Depending on the affected nerve pathway, the rash typically appears along one dermatome, which can encompass the chest, abdomen, or other regions.
How the location of the rash or bites can be a significant clue:
Recognizing the distribution pattern is crucial. Bed bug bites are often localized on areas that come into contact with bedding, while shingles follow nerve pathways. Understanding these distinctions in location can aid in accurate identification and differentiation between the two conditions.
Symptoms and Sensations
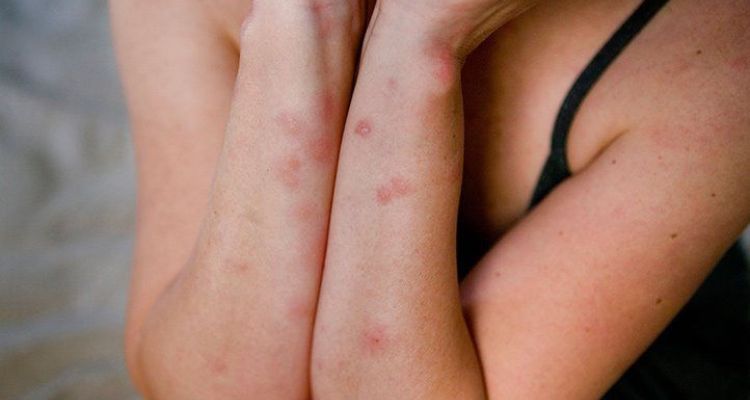
Detailed explanation of the itching and discomfort experienced with bed bug bites:
Bed bug bites cause intense itching that can persist for days or weeks. Scratching can lead to secondary infections, making them even more uncomfortable. Discomfort is primarily due to an allergic reaction to the bed bug’s saliva injected during feeding.

Description of the pain, tingling, and burning sensations commonly associated with shingles:
Shingles is characterized by excruciating pain, often described as burning, stabbing, or tingling. These sensations can be severe and are a result of the virus affecting nerve endings within the dermatome, where the rash appears.
How the sensation and severity of symptoms can differ between the two conditions:
Bed bug bites primarily cause itching and discomfort on the skin’s surface. In contrast, shingles manifest as deeper, nerve-related pain, often accompanied by severe burning or tingling sensations. Understanding the nature of these sensations helps in distinguishing between the two conditions.
Timeline and Progression
Overview of the timeline of bed bug bites, from initial bite to reaction:
Bed bug bites typically show minimal immediate reaction. It may take a few days for redness and itching to develop, reaching peak discomfort within a week. Symptoms gradually subside with proper treatment but can persist if scratching leads to secondary infections.
Explanation of the stages of shingles, including prodromal symptoms and blister formation:
Shingles follows a distinct progression, beginning with prodromal symptoms such as tingling or burning, lasting for a few days. This is followed by the emergence of a rash, which progresses from redness to blister formation. The blisters eventually crust over and heal over several weeks.
How understanding the progression can help in differentiation:
Recognizing the timeline of each condition is vital for differentiation. Bed bug bites have a delayed reaction and primarily affect the skin’s surface, while shingles follow a more structured course, with distinct stages and deeper, nerve-related symptoms. Understanding these timelines aids in accurate identification and timely intervention.
When to Seek Medical Help
Indications of when to consult a healthcare professional for shingles:
Seek medical attention if you suspect shingles, especially if you are over 50 or have a weakened immune system. Prompt treatment can help alleviate pain and prevent complications. If the rash appears near the eyes, consult a doctor immediately to prevent eye damage.

When to seek advice from a dermatologist or pest control expert for suspected bed bug bites:
If you experience persistent or severe itching from bed bug bites or if you notice signs of an infestation, consult a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment. Consider contacting a pest control expert for suspected bed bug infestations in your home.
The importance of accurate diagnosis for proper treatment:
Accurate diagnosis is paramount, as bed bug bites and shingles require different treatments. Misdiagnosis can lead to ineffective remedies and prolonged discomfort.
Seeking timely professional guidance ensures appropriate care, faster relief, and the prevention of potential complications associated with these conditions.
Conclusion
In the quest to alleviate the discomfort and concern caused by skin conditions and rashes, recognizing the differences between bed bug bites and shingles is paramount.
Bed bug bites, characterized by their clustered pattern and itching, require diligence in pest management and personal hygiene. Conversely, with their distinct dermatomal rash and nerve-related pain, shingles warrant immediate medical attention.
Timely identification of these conditions is not merely about comfort but also about health and safety. Accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment can spare individuals from unnecessary suffering, expedite their recovery, and ensure the prevention of potential complications.
Understanding these distinctions empowers individuals to take control of their well-being and seek the right guidance when needed.

