An orthopedic mattress is a mattress that is usually prescribed for patients who may be suffering from any kind of back or joint problems. They are designed to spread the body’s weight evenly over the mattress so that the buildup of pressure in different areas can be avoided, particularly the neck, back, and hips. In this article, we’ll discuss different orthopedic mattress layers, what they do, and how to select the right varieties.
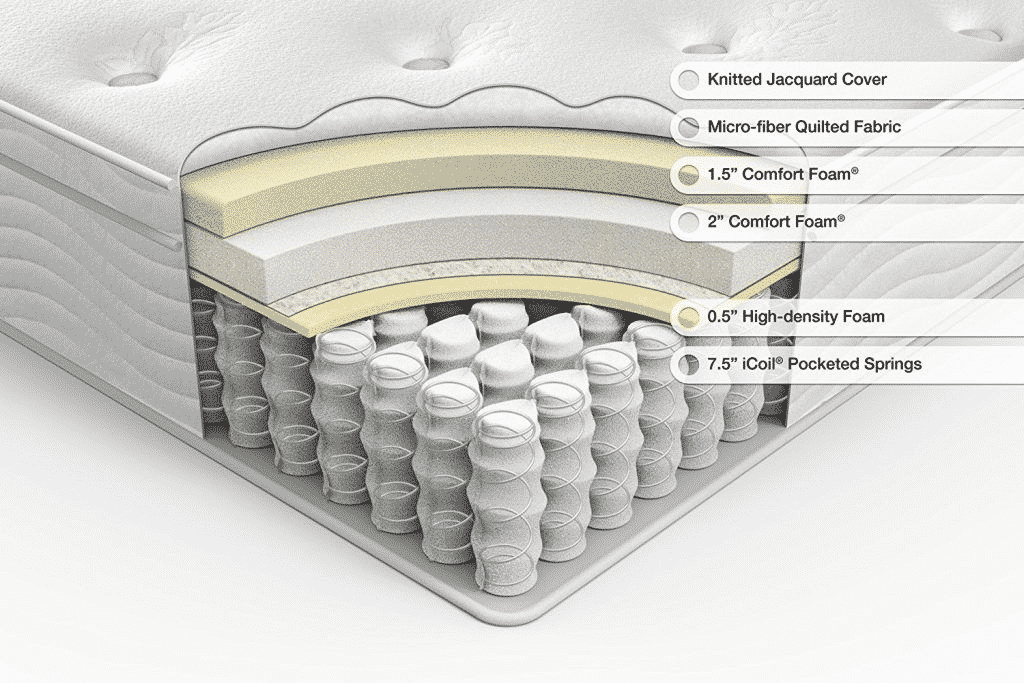
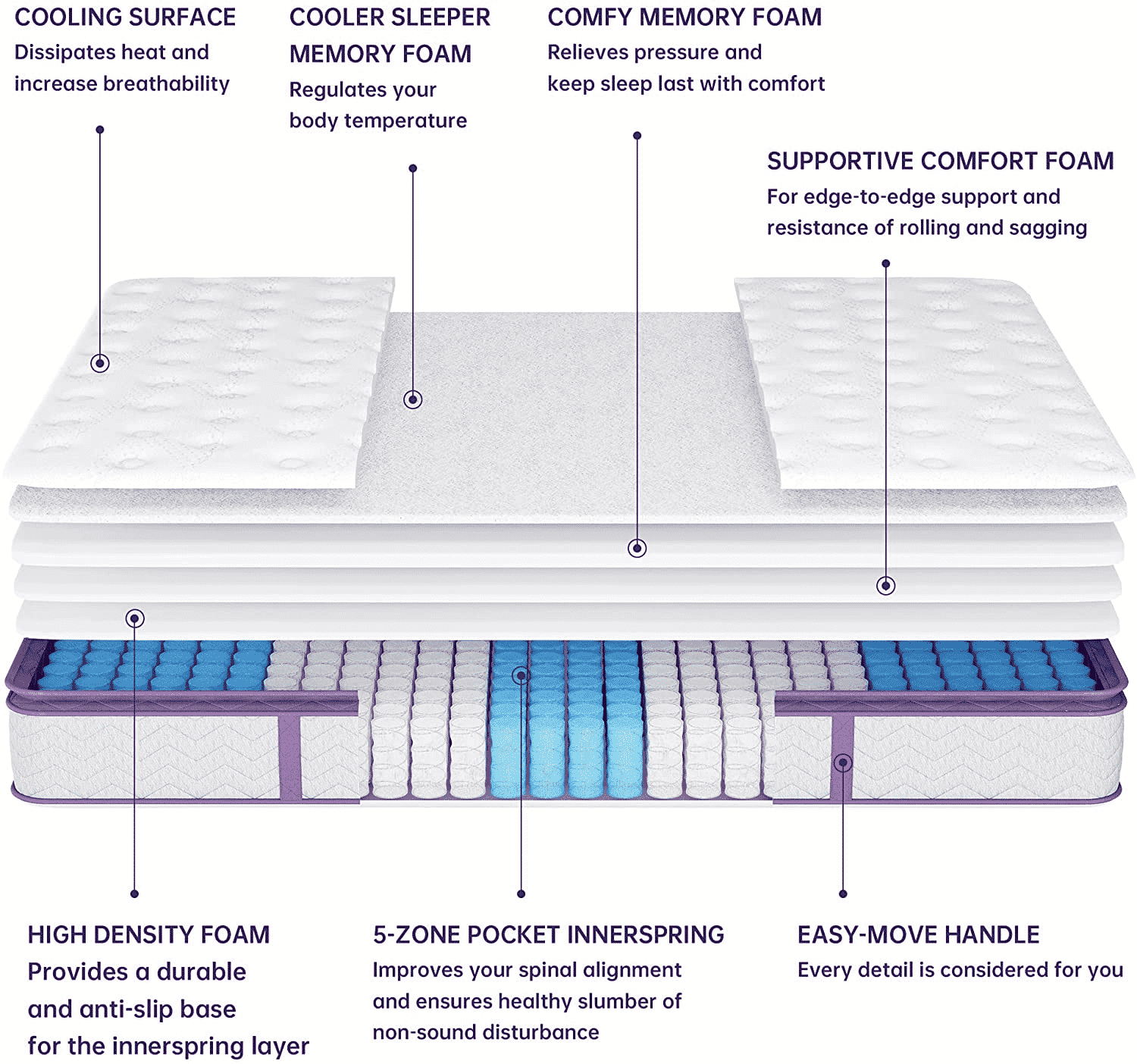
Orthopedic mattresses typically have four layers which include soft memory foam for comfort, firm memory foam for support, a foundational latex layer for support, and an innerspring layer for durability and volume.
The design of a genuine orthopedic mattress ensures correct spinal alignment to help alleviate stress on the spine and reduce back pain as we discuss in our article about the benefits of orthopedic mattresses. Most orthopedic mattresses typically have three to four layers each designed with a different purpose in order to help aid in overall pain relief and joint problems. This article from Web MD explains more about choosing a mattress that is suitable for lower back pain.
Layers of An Orthopedic Mattress
Different orthopedic mattress layers typically include innerspring, latex, and memory foam. Innerspring is the foundation layer, latex is the support layer, and memory foam molds to the shape of the body. You can find more information about choosing orthopedic mattresses in this brief background by DuroFlex, an indian mattress manufacturer.
The four structural layers of an orthopedic mattress serve different functions – soft memory foam, firm memory foam, latex, and innerspring. The soft memory foam layer provides comfort, the firm memory foam provides support and molds to the shape of the body, the latex layer is the first foundation layer, and the innerspring layer is the firm durable foundation layer that provides volume and shape.
1. Softer Layer of Memory Foam
This is the topmost layer of an orthopedic mattress that usually has a quilted cover. Although it might not seem like it serves a real purpose, it is crucial for providing just the right amount of comfort that is needed while resting. This top layer provides a plush surface and molds slightly to the shape of the neck, shoulders, back, and hips ensuring added comfort during the night. It also provides an adequate amount of support for the legs and aids in pain relief as well as tension release throughout the body.
Choosing a gel foam or gel swirl mattress will increase the breathability and allow you to sleep cooler. But if you’re a cold sleeper, choose traditional memory foam for a warmer feel.
Do not choose an orthopedic mattress with a really thick, soft, memory foam layer. These mattresses cause the spine to bend too much because they allow the sleeper to sink in, as described in this article by Amerisleep, an orthopedic mattress manufacturer.
If the layer of memory foam of the orthopedic mattress is thin, like this one, the level of comfort provided is likely to be noticeably less than a thicker layer which will provide more comfort, and a higher-density foam is more supportive and distributes weight more evenly as explained in our article that compares orthopedic mattresses vs. high-density mattresses. High-quality orthopedic mattresses like these that contain memory foam, can be purchased online.
You might also be interested in learning about the differences between an orthopedic mattress vs. a Posturepedic mattress. Be sure to read our comprehensive guide for more details.
2. Relatively Firm Memory Foam
Although the top layer of this orthopedic mattress is made from softer memory foam, the second layer is relatively firm. This is because even though the body needs the comfort provided by the top layer, it also needs support and something to stop it from sinking into the mattress (and mattress sagging). The second comparatively firm layer of memory foam serves this purpose by molding to the shape of the body and supports the parts of the body that are heaviest. This allows muscles to relax completely and helps to promote proper rest and recovery while sleeping.
If this layer is thicker and denser, the body will be getting a greater amount of support (which is valuable for heavier sleepers). Orthopedic mattresses containing memory foam like these, are readily available online.
You should choose an orthopedic mattress with strong edge support (which comes from this firm foam layer, metal wires, and additional features) because it makes the mattress more durable. Patients with back problems tend to sit on the edge of their mattress before getting in or out of bed. For this reason, the edge needs to be reinforced or it will give way and cause the mattress to start sagging and breaking down faster.
3. Latex
There is a layer of latex under the layers of memory foam which provides support and is part of the foundation of the orthopedic mattress. Latex is generally quite firm and unyielding which is what makes it ideal for use in an orthopedic mattress. Healthline explains more about the benefits of latex and memory foam in this article.
Latex helps with spine alignment as well as joint support because it does not let the body bounce back or sag into the mattress. There are no dips which also ensures that there is no build-up of pressure in any area of the body. Contrary to popular belief, latex is also quite breathable so poor air circulation is not something you need to be worried about either if you are using an orthopedic mattress containing a layer of latex. Orthopedic mattresses like these have a layer of latex.

You might also find interest in our ultimate orthopedic mattress weight guide. Be sure to check that article out as well.
4. Innerspring
The bottom of an orthopedic mattress is usually an innerspring layer and is essentially made up of steel coils providing the most support and durability. This layer is also known as the foundation of the mattress and is crucial for the complete support of the body. Typically innerspring layers within orthopedic mattresses are hinged or gatched to allow them to flex (which is especially important for hospital beds). This support enables even weight distribution and pushes back against the body to hold the spine in a neutral position.
Pocketed springs can move independently of each other vs. traditional springs which are connected and move together. Independent movement allows pocketed springs to contour better to a body vs. traditional springs which provide more support (because they push back together).
Orthopedic mattresses like these contain various innerspring layers that provide superior support.
Although the layer of innerspring usually forms the very bottom of the mattress it is also possible to choose an orthopedic mattress that can be flipped, to increase the lifespan of your mattress.

Be sure to also check out our tips for finding an orthopedic mattress without springs for additional information.
Summary of Orthopedic Mattress Layers
| Orthopedic Mattress Layers | What Purpose Do They Serve? |
| Relatively soft memory foam | Comfort. |
| Relatively firm memory foam | Comfort and Support. |
| Latex | Support and better air circulation. |
| Innerspring | Weight distribution and absorption. |
You may also find interest in learning how to find an orthopedic mattress for scoliosis. Make sure to read our related article to find out. Also, have you ever wondered what the difference is between an orthopedic mattress vs. a regular mattress or what mattresses do orthopedic doctors recommend? Take a look at our related articles to find out more.
Are All Orthopedic Mattresses The Same?
Although at first glance, it might seem like all orthopedic mattresses are the same and are manufactured in the same way, they are not. Since they are made to aid spinal alignment, support joints, and relieve pain, they need to be designed differently for specific needs.
Orthopedic mattresses are not all the same. Each mattress will have a different set of materials layered in a different order – this can impact the comfort, support, and pain relief properties of an orthopedic mattress.
The type of orthopedic mattress that you choose would depend on the materials used in the construction of its layers, as we explain in our detailed guide on orthopedic mattress materials. The material used does not necessarily have to be the same. For example, orthopedic mattresses like these will have a layer of gel foam whereas others will not. Moreover, the order in which these materials are used can vary as well. For example, sometimes the memory foam layer on the top is followed by another firmer kind of memory foam before the latex layer, but sometimes the latex layer will come first. The way that these materials are combined makes each type of mattress unique and suitable for different needs.
Make sure to also take a look at our quick comparison between orthopedic mattresses vs. latex mattresses to find out how different they might turn out to be.
Key Takeaways
Orthopedic Mattress Layer Composition
The structure of an orthopedic mattress is meticulously designed with layers including soft memory foam, firm memory foam, latex, and innerspring to cater to the need for comfort, support, and durability, particularly for individuals with back or joint issues.
Soft Memory Foam Layer
The topmost layer of an orthopedic mattress, made of soft memory foam, provides a plush surface ensuring added comfort during sleep by molding slightly to the body contours, which is pivotal for pain and tension relief throughout the body.
Firm Memory Foam Layer
Beneath the soft memory foam, the firm memory foam layer serves to prevent the body from sinking into the mattress, providing the requisite support that aids in proper rest and muscle relaxation during sleep, which is particularly beneficial for heavier sleepers.
Latex Layer
The latex layer, positioned under the memory foam layers, is instrumental in providing firm support, aiding in spinal alignment and joint support, and ensuring breathability, making it a vital component of an orthopedic mattress.
Innerspring Layer
The foundational innerspring layer at the bottom provides robust support and durability to the mattress, facilitating even weight distribution and holding the spine in a neutral position, which is crucial for individuals with back or joint discomfort.
Variability in Orthopedic Mattresses
Not all orthopedic mattresses are identical; the arrangement and types of materials used in the layers can vary, impacting the level of comfort, support, and pain relief provided. Hence, choosing an orthopedic mattress should align with individual needs and preferences concerning the material composition and layer arrangement.
Individualized Needs and Selection
Orthopedic mattresses are tailored to meet specific needs for spinal alignment, joint support, and pain relief. The selection should hence be based on individual medical conditions, comfort preferences, and the particular attributes of the mattress layers, ensuring it adequately addresses the user’s requirements.

